
Materials Ecosystem
Unlocking the Value of Waste
Dow’s approach for a better way to make, use and reuse plastics.
What is the materials ecosystem?
By definition, waste is unwanted, requires disposal and is not always valued. However, when science and economics find a way to take this unwanted material, break it down into its basic building blocks and turn those building blocks into something useful again, plastic waste is transformed and takes on value.
A materials ecosystem is developing around plastic and renewable waste to deliver its total value. The materials ecosystem adds value to plastic waste through recycling technologies and circular solutions.
By repeatedly converting plastic waste into new products, less waste ends up in landfills, incinerators or as environmental leaks.
How does the materials ecosystem function and support transformation?
Waste transformation counts on the materials ecosystem elements working together, from infrastructure to partners and technologies.
Influences such as consumer behavior and the regulatory landscape are complex and affect the materials ecosystem at local, regional, and global levels.
Disconnects in the materials ecosystem present opportunities to innovate and collaborate.
Explore the elements of the materials ecosystem
Mechanical recycling is a process, by which plastic waste is turned into new products without the structure being significantly altered. Plastic manufacturers can use this material in applications with less performance needs, such as trash bags, rigid plastic containers and building materials.
Featured collaborations
To enable broader use of recycled plastic, Dow is investing in advanced recycling. Advanced recycling offers massive, untapped market potential and the ability to bring circularity to previously incompatible areas such as food-grade and medical-grade packaging by using the same material for reuse.
Featured collaborations

To produce new plastic materials that are more sustainable — and reduce the use of fossil feedstocks and the carbon footprint associated with them — it will take a combination of feedstocks produced from recycled plastic waste and bio-circular materials. Dow focuses on non-edible renewable resources.
Featured collaborations
New Energy Blue
Ecolibrium™ - Bio-circular materials

There is a gap between downstream demand for circular plastics and available supply. The local players in waste management, recycling, design and manufacturing are essential to waste reaching its full potential through local recycling options, infrastructure, education and incentives.
Featured collaborations

Design is indispensable to supporting markets in transforming materials use for less environmental impact. Brand owners and manufacturers must consider tradeoffs between cost and performance while ensuring that product integrity remains intact. Learn how we can meet targets to enable recyclability.
Featured collaborations

Improving recycling requires understanding what drives behavior and creating conditions that support the recycling behavior we seek. Dow’s environmental nonprofit partners — including the Alliance To End Plastic Waste, The Recycling Partnership, Delterra and others — are demonstrating that behavior change is possible.
Featured collaborations
Dow is investing approximately $1 billion annually to drive growth & decarbonization of our manufacturing assets by replacing end-of-life, carbon-intensive assets with more carbon-efficient and carbon abatement technologies, such as circular hydrogen, nuclear and carbon capture and storage.
Featured collaborations

Policymakers, investors, and non-profit organizations are the global tailwinds enabling circular supply chains.
Featured collaborations

Dow’s perspective on the materials ecosystem
The dynamics of waste are changing. Read how.
Published in October 2023

Chapter 1
Eco-conscious consumers: How purchasing power drives systems change.

Chapter 2
It starts with design: How circularity “by design” is accelerating.

Chapter 3
Finding value in waste: Signs of progress in waste collection and recycling.

Chapter 4
Material origins: How inventive recovery technologies are transforming more plastic into high-value waste.
How do we transform waste into a valuable resource?
The world demands a better way to make, use and reuse plastics. Dow sees a way.
The materials ecosystem: Unlocking the value of waste
We’re talking about the materials ecosystem and Dow’s approach for a better way to make, use and reuse plastics. Learn how a materials ecosystem is developing around plastic and renewable waste to deliver its total value.
Collaborating to drive progress
It takes every stakeholder working together to make change happen, including new technologies to transform waste into products; recycling infrastructure that delivers on the ecosystem's ability to collect, clean and sort waste; policy that enables systems to scale and succeed; brands and manufacturers designing for circularity; and consumers having the confidence that their efforts to return used plastic to the system will pay off.
Materials ecosystem resources

We're working across industries to deliver solutions that help our customers meet their sustainability targets and goals.

A global plastic pollution agreement can incentivize circularity and enhance waste management infrastructure.

Haley Lowry, Director of Sustainability, talks waste transformation with Dow collaborators at the Fast Company Innovation festival.
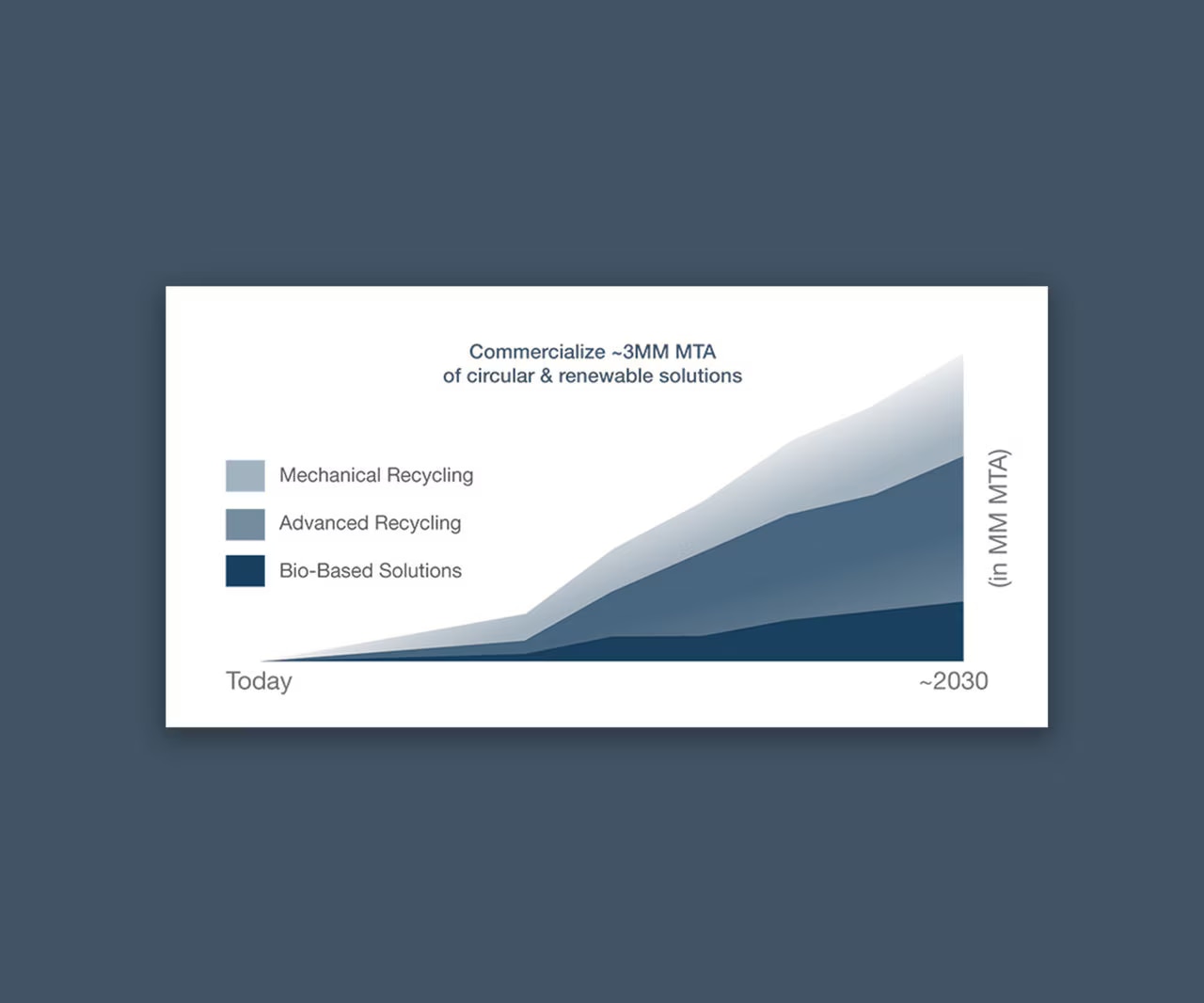
Read the full Dow progress report to learn how we're accelerating our roadmap to Transform the Waste.

Stay informed on circular polymers
Learn more about the latest innovations and technologies capturing the value of plastic for a more sustainable world.
Get in touch to collaborate with us

